
What is Battery Energy and How Does It Impact Renewable Energy Systems
As the world increasingly transitions towards renewable energy systems, understanding the role of battery energy has become paramount. Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are crucial for enhancing the stability and reliability of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. According to a report by the International Energy Agency (IEA), energy storage capacity is projected to increase significantly, reaching 200 gigawatt-hours by 2030. This growth underscores the importance of battery energy in enabling grid flexibility and integrating intermittent renewable sources into the energy mix.
Battery energy not only facilitates the storage of excess energy generated during peak production periods but also provides backup power during fluctuations in demand. Research indicates that effective battery solutions can reduce reliance on fossil fuels, potentially leading to a 70% reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by 2050 if adopted widely. Furthermore, the implementation of advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, is poised to enhance the efficiency and longevity of energy storage systems. As policymakers and industry leaders focus on achieving sustainable energy goals, the advancement of battery energy will play a vital role in fostering the resilience of renewable energy systems and ensuring a greener future.
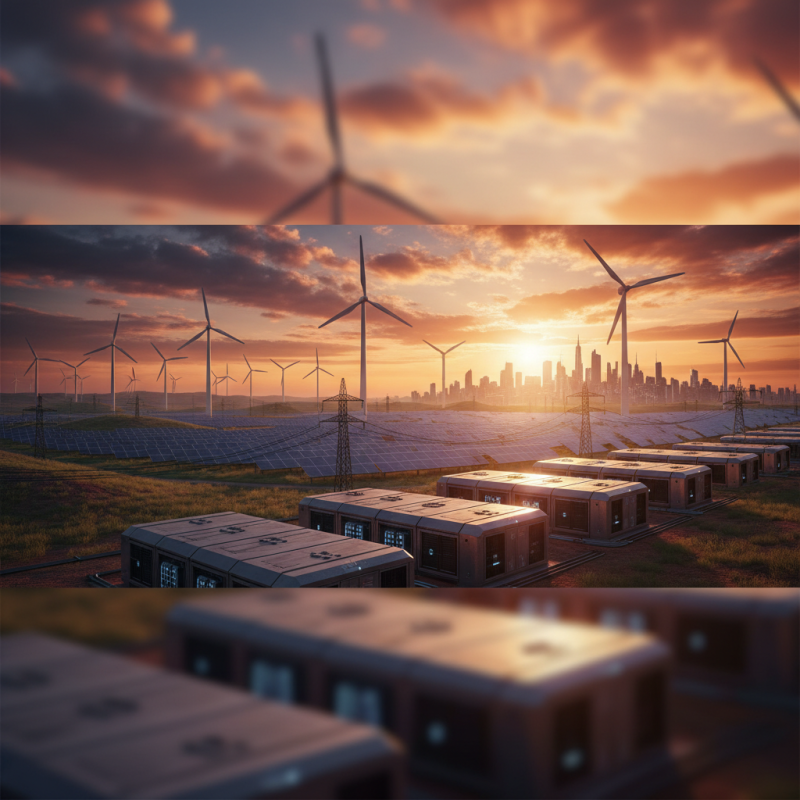

Definition of Battery Energy and Its Role in Energy Storage
Battery energy refers to the stored electrical energy in a battery that can be released to power devices, facilitate renewable energy integration, and stabilize energy grids. In the context of energy storage, battery energy plays a critical role by capturing excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar or wind, during peak production periods. This stored energy can then be deployed during times when generation is low or demand is high, ensuring a steady and reliable supply.
The effectiveness of battery energy systems in renewable energy applications is pivotal for the transition to a sustainable energy future. They not only help mitigate the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources but also provide essential grid services, including frequency regulation and load balancing. By enhancing the reliability and efficiency of energy systems, battery energy contributes significantly to the overall success of renewable energy integration, enabling decarbonization goals and reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
Types of Batteries Used in Renewable Energy Systems
In modern renewable energy systems, the type of batteries employed plays a crucial role in optimizing energy capture, storage, and utilization. Lithium-ion batteries are among the most popular choices due to their high energy density and efficiency. According to a report from the International Energy Agency (IEA), lithium-ion battery costs have decreased by more than 80% since 2010, making them substantially more affordable for large-scale renewable energy projects. These batteries can store energy generated from sources like solar and wind, helping to balance supply and demand effectively.
Another significant type of battery utilized in renewable systems is the lead-acid battery, which has been in use for over a century. While they are generally less efficient and have a shorter lifecycle compared to lithium-ion batteries, their low cost and reliability make them suitable for certain applications, particularly in off-grid systems. The U.S. Department of Energy has noted that lead-acid batteries are still widely used in energy storage, accounting for approximately 40% of the total energy storage capacity in the U.S. as of 2022. However, the shift towards more sustainable energy solutions is propelling innovations in battery technology, including the development of flow batteries and solid-state batteries, which promise longer lifespans and safer operation in renewable applications.
Impact of Battery Energy on Renewable Energy Efficiency
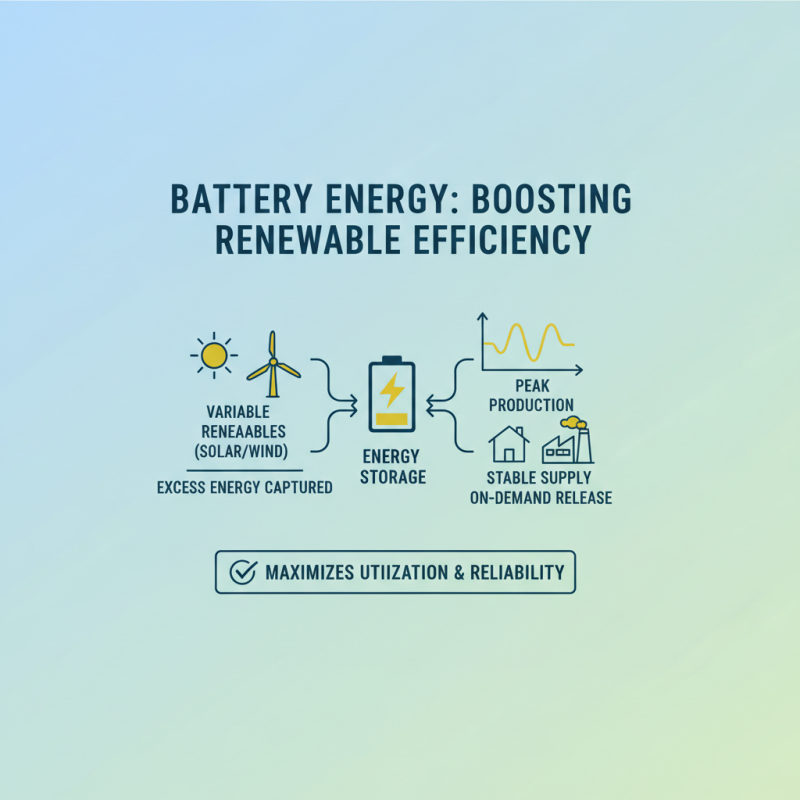
Battery energy plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of renewable energy systems. As renewable sources such as solar and wind are inherently variable, energy storage solutions are essential for managing the supply-demand balance. Batteries allow for the capture of excess energy generated during peak production times and release it during periods of low generation. This capability not only maximizes the utilization of generated renewable energy but also ensures a stable and reliable supply.
The integration of battery energy systems into renewable infrastructure can significantly reduce energy wastage and improve overall system efficiency. By enabling grid-scale storage, batteries can smooth out fluctuations in energy production, which is vital for maintaining the stability of power grids that rely heavily on intermittent energy sources. Additionally, the ability to store energy promotes the use of renewable sources during off-peak times, thereby reducing reliance on fossil fuel-based backup power and contributing to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Enhanced battery technology continues to evolve, leading to increased capacity and reduced costs, further amplifying the positive impact on renewable energy efficiency.
Challenges and Innovations in Battery Technology for Sustainability
The advancement of battery technology is critical for enhancing the sustainability of renewable energy systems. As the world increasingly shifts toward renewable sources like solar and wind, energy storage solutions face numerous challenges, particularly in efficiency, capacity, and lifespan. Recent reports indicate that while battery efficiencies have improved, with some lithium-ion batteries now offering energy densities above 250 Wh/kg, the need for innovative approaches is vital to meet the projected demand for energy storage in the coming years, which is expected to surpass 1,000 GWh by 2025 (BloombergNEF).
Innovations in battery technology, including solid-state batteries and flow batteries, are being explored to overcome current limitations. Solid-state batteries promise to enhance safety and energy density significantly, paving the way for more effective integration with renewable energy systems. In contrast, flow batteries offer advantages in scalability and longevity, making them suitable for large-scale energy storage solutions necessary for balancing intermittent energy sources. As the International Energy Agency suggests, encouraging research and development in these technologies could lead to cost reductions of up to 50% by 2030, ultimately transforming how renewable energy can be harnessed and utilized on a massive scale.
Future Trends in Battery Energy for Renewable Energy Integration
The integration of battery energy storage systems (BESS) is becoming increasingly vital for enhancing the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems. This trend is reflected in the significant growth of the global battery energy market, which is projected to reach approximately $140 billion by 2025, according to a report by ResearchAndMarkets. As renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are inherently intermittent, the ability to store excess energy generated during peak production times for later use is essential for maintaining grid stability and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Future trends indicate that advancements in battery technology, including the development of solid-state batteries and improved lithium-ion solutions, are set to transform energy storage capabilities. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) forecasts that battery storage capacity could increase to 1,200 GWh by 2030, paving the way for a more resilient grid structure. Additionally, the advent of decentralized energy generation and increased consumer participation in energy markets are creating opportunities for innovative applications of battery storage, such as vehicle-to-grid technology, which allows electric vehicles to contribute to grid stability. As investments in R&D continue to rise, the synergy between battery energy and renewable systems will prove crucial in driving the transition towards a sustainable energy future.
Battery Energy Capacity Trends in Renewable Energy Systems
This chart illustrates the increasing energy capacity of batteries in renewable energy systems from 2018 to 2023. The trend indicates a significant growth in battery storage capacity, essential for enhancing the integration of renewable energy sources.
Related Posts
-

The Rise of Power Battery Technology Transforming Sustainable Energy Solutions
-

Why Power Batteries Are Essential for the Future of Renewable Energy: Key Insights and Trends
-

Unlocking the Secrets Behind High Battery Technology for Your Everyday Devices
-

What Is a Better Battery? Key Features and Benefits Explained
-

2025 Top Energy Battery Trends Driving the Future of Sustainable Power Solutions
-
Unleashing the Power of Battery Energy for Sustainable Living in the Digital Age
- © 2025 Northeast Battery


Northeast Battery, a Stored Energy Holdings, Inc. Company